A succession of FET-like devices was patented by Julius Lilienfeld in the 1920s and 1930s. However, materials science and fabrication technology would require decades of advances before FETs could actually be manufactured. JFET was first patented by Heinrich Welker in 1945. During the 1940s, researchers John Bardeen, Walter Houser Brattain, and William Shockley were trying to build a. Because a reasonably high dose of estrogen is taken from day 2 of your cycle in an FET protocol, the hormone is a down-regulator and prevents ovulation. Introduction: FET is the short form of Field Effect Transistor. It is called unipolar transistor as current flow is carried out by majority charge carriers only. FET transistor is controlled by voltage rather than current unlike BJT. Refer FET versus BJT. Following are the advantages of FET over BJT. FET (Field-Effect Transistor) Basics Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) are unipolar devices, and have two big advantages over bipolar transistors: one is that they have a near-infinite input resistance and thus offer near-infinite current and power gain; the other is that their switching action is not marred by charge-storage problems, and they thus outperform most bipolars in terms of digital switching speeds.
On May 23, Susan B. Anthony List and Charlotte Lozier Institute hosted a hearing for Capitol Hill staff on the state of fetal issue research. The panel consisted of Drs. David Prentice, Tara Sander Lee, and James Sherley, and was moderated by SBA List’s Autumn Christensen. These are their questions and answers, as provided to staff.
Q1: In the late 1980s and early 1990s Congress was embroiled in a fight over fetal tissue transplantation. What happened during that fight and what is the difference between fetal tissue transplantation and basic research using baby body parts?
In 1988, President Reagan placed a moratorium on federal funding of transplantation research using aborted fetal tissue. That moratorium remained in place until lifted by President Clinton in January 1993. Subsequently, Congressman Waxman led an effort that resulted in a statute that says, “The Secretary may conduct or support research on the transplantation of human fetal tissue for therapeutic purposes.” [42 U.S.C. 289g-1 and g-2]
Two large controlled trials were finally funded to transplant aborted fetal brain tissue into Parkinson’s patients. Those results, which came out in 2001 and 2003, showed that fetal tissue transplants did not help patients and actually made many patients worse. The New York Times front-page story contained the doctors’ descriptions of patients writhing, twisting, and jerking with uncontrollable movements; the doctors called the results “absolutely devastating,” “tragic, catastrophic,” and labeled the results “a real nightmare.” The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is required to report to Congress its funding of fetal tissue research; it has not funded anyclinical trials with fetal tissue in over a decade.
The only real success for transplants has come from adult stem cells, which have already helped roughly 2 million people, for dozens of diseases and conditions.
Basic laboratory research using fetal tissue is not covered by the statute. Federal funding of basic research is allowed at the discretion of the Director of NIH. Current taxpayer funding is approximately $120 million per year.
Resources for Question 1:
- Gina Kolata, “Parkinson’s Research Is Set Back by Failure of Fetal Cell Implants,” New York TimesMarch 8, 2001; accessed at: http://www.nytimes.com/2001/03/08/health/08PARK.html
- Freed CR et al., Transplantation of embryonic dopamine neurons for severe Parkinson’s disease, N Engl J Med344, 710, 2001
- Olanow CW et al., A Double-blind Controlled Trial of Bilateral Fetal Nigral Transplantation in Parkinson’s Disease, Ann Neurol54, 403, 2003
- Prentice DA, Adult Stem Cells: Successful Standard for Regenerative Medicine, Circulation Research124, 837-839, 15 March 2019.
Q2: In the summer of 2015, the Center for Medical Progress released videos exposing the sale of baby body parts. These undercover videos showed Planned Parenthood staff discussing abortion procedures with individuals they believed to be interested in buying baby body parts for research. These videos kicked off a national awareness of the gruesome process of trading in baby body parts and even the potential for babies to be born alive and harvested for research – leading to the Born Alive Abortion Survivors Protection Act. What has come of these revelations?
The undercover work of the Center for Medical Progress (CMP) reveals a cynical culture of disregard for human fetuses as innocent human beings by high-level executives and senior abortion performers in Planned Parenthood (PP). In fact, some Planned Parenthood sites were revealed to be knowingly conducting illegal trade in human fetal tissue with commercial buyers. However, what is most troubling about the revelation of the CMP tapes is the recorded abortion providers’ bland attitudes towards aborted fetuses as faceless commodities for sale, and in some cases for personal benefit, without any expressed sense of compassion or concern for either the aborted infants or their mothers.
In 2017, the LA Times reported that two related companies in California, DaVinci Biosciences and DV Biologics, “reached a $7.785-million settlement with the Orange County district attorney’s office over allegations that they illegally sold fetal tissue to companies around the world.” The same companies were featured in the CMP tapes for sourcing fetal tissue from Planned Parenthood. “The agreement also [required] the companies to admit liability for violations of state and federal laws prohibiting the sale or purchase of fetal tissue for research purposes…”
StemExpress, a biomedical tissue procurement firm that previously sourced electively aborted fetal tissue from Planned Parenthood, severed its ties with PP in the wake of the CMP tapes. The company no longer lists fetal tissues at its website.
Advanced Bioscience Resources (ABR) is an even more troubling case that was brought to light as a result of the CMP investigation. This company was contracted by the U.S. FDA to source fetal tissue from PP for use in government biomedical research. Though ethically objectionable, these transfers would still have been legal, except that ABR may have intentionally operated at a profit, which is illegal. U.S. Health and Human Services has since revoked the FDA contract with ABR, and the U.S. Department of Justice is now investigating ABR for criminal wrongdoing.
Q3(a): What about vaccines. Is that why these tissue brokers buy the organs and tissues of unborn babies?
No, the historical fact is that fresh aborted fetal tissue has never been used in vaccine production. The original Salk and Sabin polio vaccines used monkey tissue to grow virus. While there are a couple of historical cell lines that were grown from abortions in the 1960s, kept in cell culture, and used for some vaccines, even these cell lines are obsolete and no longer used for most vaccines today. For example, much of the polio vaccine today is made using the Vero monkey cell line.
Q3(b): If fetal tissue is not used for vaccines, what methods are used for vaccine production today and what are some of the new vaccine technologies?
Many modern vaccines use animal cell lines, even insect cell lines, as well as modern human cells that are not from fetal tissue. As just a couple of examples, the new Ebola vaccine– recently shown to be 97.5% effective – is produced using the Vero monkey cell line, and the recently approved shingles vaccine (Shingrix) which is a modern recombinant subunit vaccine produced in engineered hamster cells, also than 90% effectivenesswhile providing better protection than the historical vaccine produced in fetal cells.
Resources for Question 3:
- Helen Branswell, “The data are clear: Ebola vaccine shows ‘very impressive’ performance in outbreak” STATnews, April 12, 2019; https://www.statnews.com/2019/04/12/the-data-are-clear-ebola-vaccine-shows-very-impressive-performance-in-outbreak/
- Nordén R et al., Recombinant Glycoprotein E of Varicella Zoster Virus Contains Glycan-Peptide Motifs That Modulate B Cell Epitopes into Discrete Immunological Signatures, J. Mol. Sci. 20, 954, 2019.
Q4(a): If NIH is not funding aborted fetal tissue research for vaccines, what basic research is being funded?
NIH funds both intramural (on the NIH campus or other NIH facilities) and extramural (off campus, often at a university) fetal tissue research. In FY 2018 NIH spent $115 million on grants involving human fetal tissue research and is estimated to spend $120 million in FY 2019. Most of these grants are extramural, but roughly $21 million is intramural research. NIH also gives out millions of federal dollars in contracts for specific projects using fetal tissue.
Projects funded for fetal tissue research include studies on normal and abnormal development, including brain development, retinal formation and degeneration, and infectious diseases including HIV infection. Note that this means NIH and its researchers are purchasing aborted fetal brains, eyes, livers, hearts, and other organs for these studies.
Q4(b): Are there alternatives to use of aborted fetal tissue in research?
There are many alternatives. One is use of miscarried tissue, which can be used to study development as well as causes of pregnancy loss. A modern alternative is use of what are called “organoids,” which are constructed from adult stem cells and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. Organoids are organ-like structures and tissues that have been shown to mimic normal development and can also be used to study abnormal development and causes of birth defects. Adult stem cells, iPS cells, and postnatal tissue (neonatal and adult) can also be used to study infectious diseases and therapies, including construction of “humanized mice” to study infections.
Resources for Question 4:
- Kretzschmar K and Clevers H, Organoids: Modeling Development and the Stem Cell Niche in a Dish, Cell38, 590-600, September 26, 2016, DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.08.014
Q5: The Zika virus is believed to have a direct effect on the growing brains of unborn children. The concern is that if a pregnant mom is bitten by a mosquito carrying Zika, the baby may develop something called microcephaly which shrinks their brains. Is fetal tissue research necessary to learn more about Zika?
Because the Zika virus infects the brains of babies in utero, some researchers want to obtain brains of aborted babies (usually 9-13 weeks’ gestation) in order to study viral infection. Some researchers perform direct observational studies on the brains while others will isolate stem cells from the tissue to study the mechanism of infection.
We know from published studies that organoids, three-dimensional organ-like structures constructed using modern stem cell techniques, are incredible models for studying Zika infection. These organoids have been instrumental in deciphering both normal brain development and the mechanism of Zika virus action on the developing brain. In one example, a seminal study in the journal Scienceshowed that brain organoids can recapitulate the mechanism of how Zika infects human cells and causes the same microcephaly observed in humans.

Resources for Question 5:
- Garcez PP et al., Zika virus impairs growth in human neurospheres and brain organoids, Science2016, 352:6287
Q6: A University of California San Francisco (UCSF) contract for baby body parts has gotten a lot of attention. What is that contract for?
NIH has given a multi-year contract to UCSF for production of a type of humanized mouse that contains a human immune system, to study HIV infection and potential HIV drugs. The total amount of this contract, through December 5, 2020, is $13,799,501; NIH has so far paid over $10 million. The project uses aborted baby livers, thymus, bone marrow, and intestinal tissue, and the contract calls for use of organs from at least 24 aborted “donors” per year. In fact, NIH requires the use of aborted fetal organs in this contract. NIH renewed the contract for 90 days in December 2018, and again in March 2019. It is up for possible renewal in June, just days away.
Q7(a): What are humanized mice?
Humanized mice are mice with a human immune system. These mice are severely immune compromised and unable to fight off infection and disease, but researchers are able to regenerate a functional human immune system in these mice by engrafting (transplanting) human immune cells and tissues derived from fetal or non-fetal sources.
Apple os updates in order. There are several ways to make a humanized mouse. The process involves transplantation of human tissue and/or injection of human cells directly into the mouse. The bone marrow/liver/thymus “BLT” mouse model is generated by implanting dissected human fetal liver and thymus (16-22 weeks’ gestation) under the kidney capsule of the mouse and injecting CD34+ blood stem cells from the remaining liver of the same fetus into the mouse tail vein.
Run docker image on windows. Humanized mice are used to study immune response to human-specific infections and disease, such as HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, Dengue, Epstein-Barr Virus, and cancer, as well as to test new therapeutic drugs. Human fetal bone fragments are also transplanted into mice to study multiple myeloma.
Q7(b): Are all humanized mice bad? Are there other ways to make humanized mice?
No, they’re not all bad. There are many ways to make humanized mice using cells and tissues from adults and discarded tissues, without killing the fetus to harvest its tissue. For example, humanized mice can be generated using peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), often referred to as the “hu-PBMC” or “hu-PBL” mouse. Another model is called the “hu-HSC” mouse, generated using CD34+ hematopoetic (blood) stem cells (HSCs), which can be obtained from bone marrow, cord blood, and peripheral blood. A newer option, called the “NeoThy” mouse uses neonatal thymus tissue from surgical procedures, which is 50 times more efficient and 1,000 times more cost effective than aborted fetal tissue for generating the same number of mouse models.
References for Question 7:
- Brown ME et al., A Humanized Mouse Model Generated Using Surplus Neonatal Tissue, Stem Cell Reports, 2018, 10(4):1175-1183
Q8(a): Hasn’t fetal tissue research been used to find breakthroughs for HIV? Isn’t continued research necessary to learn more about and treat HIV/AIDS?
Some claim that fetal tissue is “needed” because BLT humanized mice generated with fetal bone marrow/liver/thymus tissue have been used to study HIV infection, human immune response, and antiretroviral treatments, and to test new therapies (i.e., Truvada). However, the BLT mouse is only one model among many other animal and non-fetal models that have been used to study HIV. Therefore, humanized BLT mice were not the only means available to understand the mechanism of HIV infection and test safety and efficacy of therapies before use in humans.
Q8(b): Can those goals be achieved using alternative research methods?
Absolutely. First, we don’t need fetal tissue to make humanized mouse models. We can use peripheral blood, cord blood, bone marrow, and neonatal thymus tissue, as discussed earlier. In fact, a recent study by Cheng et al. (2018) showed that the hu-HSC alternative mouse model is sufficient, meaning we don’t need fetal tissue, for the study of HIV infection, pathogenesis, and therapy. And hu-PBMC mice are an ideal model for rapid drug discovery and were used in early testing of therapeutics including Enbrel for rheumatoid arthritis.
Second, there are several other model systems available to researchers for studying HIV, including nonhuman primates, which are considered the most relevant animal model for HIV/AIDS research to date.
Finally, severalexamples exist of non-fetal sources used in the production of currently approved biotherapeutic agents including plant cells, insect cells, bacteria, yeast, Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, murine cells, and HT-1080 cells (created from a tissue biopsy of a fibrosarcoma from a 35-year-old human male). In fact, CHO cells are the “workhorses behind more than half of the top-selling biologics on the market today,” including Humira for arthritis and Crohn’s disease, Herceptin and Perjeta for breast cancer, Avastin for metastatic colorectal cancer, Rituxan for six diseases including chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, Prolia for osteoporosis, and Xolair for asthma, just to name a few.This does not include insulin made in bacteria and yeast to treat diabetes, and more than 70 successful treatments developed using adult stem cell sources.
If we stop harvesting aborted fetal tissue today and focus solely on alternatives, it will not stop one person from being treated.
Resources for Question 8:
- Cheng et al., Humanized mice engrafted with human HSC only or HSC and thymus support comparable HIV-1 replication, immunopathology, and responses to ART and immune therapy. Immunol., 9:817, 2018
- Dumont et al., Human cell lines for biopharmaceutical manufacturing: history, status, and future perspectives. 36:1110,2015 https://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/pressrelease/researchers_develop_new_tools_to_optimize_cho_cell_lines_for_making_biologi
Q9: With all of these advanced alternatives available, why do researchers still want fetal tissue?
That’s a good question. It doesn’t make sense. Even if we look only at the use of fetal tissue for generating humanized mice, we know that there are several advantages to using alternatives—the mice are easier to prepare at lower cost, more animals can be generated per cohort, there is negligible graft-versus-host disease and longer life span, chronic HIV infection is longer-lasting, and long-term safety and toxicity assessments are possible (Akkina et al., 2016). Humanized mice generated with fetal tissue are more technically difficult, costly, time consuming, and not as efficient as the other models (Cheng, 2018).
In short, researchers still want fetal tissue because it’s entrenched in the scientific culture and they continue to receive federal dollars to keep the research going. But the tide is shifting, and newer and better models are now available. Areport by Akkina (2013) reviewed the history of HIV research using humanized mice models and stated that “BLT mice received more attention until recently due to its early application,” but in fact, hu-HSC (non-fetal) humanized mice are “equally amicable for testing microbicide and oral pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) strategies against vaginal HIV-1 transmission.” So basically, fetal tissue is what they’re used to working with, so they continue to do so.
Another reason is that fetal tissue is often more accessible to researchers through third party vendors compared to alternative tissue. It is much easier for a researcher to “click and purchase” fetal tissue and its derivatives directly from ABR or StemExpress, rather than establishing their own protocol for patient consent, tissue procurement, and storage. Furthermore, not all researches have access to tissue banks and not all institutions perform surgeries that make specific tissue alternatives available (such as neonatal thymus tissue from cardiac procedures).
Resources for Question 9:
- Akkina, R., et al. New generation humanized mice for virus research: Comparative aspects and future prospects. Virology. 435: 14, 2013
- Akkina, R. et al., Improvements and limitations of humanized mouse models for HIV research: NIH/NIAID “meet the experts” 2015 workshop summary. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses, 32:109, 2016
- Cheng et al., Humanized mice engrafted with human HSC only or HSC and thymus support comparable HIV-1 replication, immunopathology, and responses to ART and immune therapy. Immunol., 9:817, 2018
Q10: Without federal funding of human fetal tissue research, life-saving research will be stopped. Isn’t that unethical and unfair to patients?
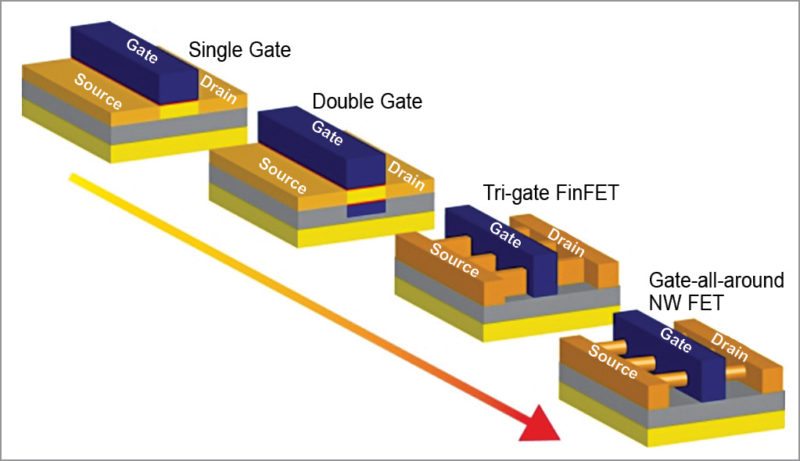
A10: This is one of the most unsupportable arguments we hear. If federal funding for fetal tissue stopped at this very moment, it would not stop any life-saving treatments.There is no form of biomedical research that is absolutely necessary for any desired advance. If that were true, we would not have made the many wonderful advances in biomedical science that we now enjoy and even take for granted. Scientific discovery can be engineered or serendipitous, and serendipity abounds. We often make life-changing discoveries in places where we never expected, and the best discoveries are those that are revealed by multiple approaches. Respecting the bodies of our presently misfortunate innocents is not going to cost us anything. It is going to improve us.
Q11: These babies would die anyway, so why not bring some good out of it?
Though seemingly pragmatic, this attitude is certainly not a moral one, as defined by having regard for the essentiality of human life in civilized human societies. Actually, it is not pragmatic either, because the stated position depends on a fallacy, that the means are necessary. But elective abortions are not necessary. They are elective. These babies would not die anyway, and the CMP revelation of the true face of PP teaches us that the desired end can soon begin to dictate the means, motivating a demand for more electively aborted human beings.
Q12: But isn’t science about exploring every option?
Never was and never will be. For example, in drug development research, we have regulations to prevent “options” that would cause harm to clinical trial subjects and future patients. All government-funded research is subject to rules and regulation that safeguard both the born and the unborn (i.e., the embryos and fetuses of pregnant research subjects) from research “options” that might cause undue injury or death. So, we have never and never will allow scientific research to be boundless. The continuing challenge, of course, is deciding as a society where to set those bounds for everyone. And in most cases, as now, the most important consideration for defining limits on science will be the quality of our regard for our impacted fellow human beings when we anticipate personal benefits at their expense.
FET, Field Effect Transistor Circuit Design Includes:
FET circuit design basicsCircuit configurationsCommon sourceCommon drain / source followerCommon gate
Field effect transistors are used in circuit design as they are able to provide very high input impedance levels along with significant levels of voltage gain.
Use Of Fet
Unlike the bipolar transistor which is a current controlled device, the field effect transistor is voltage controlled. This makes the way FET circuits are designed rather different to the way bipolar transistor circuits are designed.
However, circuits with current and voltage gain can still be designed and similar circuit formats are adopted.
FET circuit basics
When considering the use of a FET circuit, it is necessary to consider FET technology and the type of field effect transistor will be the most applicable.
Note on Field Effect Transistor Technology:
Use Of Fetus In Vaccines
The field effect transistor, FET, is a three terminal device which provides voltage gain. Having a high input impedance the electric field in the vicinity of the input terminal called the gate modifies the current flowing in what is called the channel between terminals called the source and drain.
Read more about the Field Effect Transistor Device & How it Works
The FET has three electrodes:
- Source: The Source is the electrode on the FET through which the majority carriers enter the channel, i.e. at acts as the source of carriers for the device. Current entering the channel through the source is designated by IS.
- Drain: The Drain is the FET electrode through which the majority carriers leave the channel, i.e. they are drained from the channel. Conventional current entering the channel via the drain is designated by the letters ID. Also Drain to Source voltage is often designated by the letters VDS
- Gate: The Gate is the terminal that controls the channel conductivity, hence the level of voltage on the gate controls the current flowing in the output of the device.
FET circuit design parameters
When starting out on the design of a FET circuit, it is necessary to determine the basic requirements for the circuit. These will govern many of the decisions regarding the type of circuit topology to use and also the type of FET to use.
There can be a number of parameters required in the requirements for the transistor circuit design:
- Voltage gain: The voltage gain is often a key requirement. It is the output signal voltage divided by the input signal voltage.
- Current gain: This is the gain of the FET circuit in terms of current. It may be necessary to drive a high level of current into the load.
- Input impedance: This is the impedance that the previous stage will see when it is providing a signal to this FET circuit in question. FETs inherently have a high input impedance to the gate and therefore FETs are often used where this is of paramount importance.
- Output impedance: The output impedance is also important. If the FET circuit is driving a low impedance circuit, then its output must have a low impedance, otherwise a large voltage drop will occur in the transistor output stage.
- Frequency response: Frequency response is another important factor that will affect the FET circuit design. Low frequency or audio transistor circuit designs may be different to those used for RF applications. Also the choice of the FET and capacitor values in the circuit design will be greatly affected by the required frequency response.
- Supply voltage and current: In many circuits the supply voltage is determined by what is available. Also the current may be limited, especially if the finished FET circuit design is to be battery powered.
FET types for circuit design
Anaconda python install mac. As there are several different types of field effect transistor that can be used, it is necessary to define at least some of the FETs that can be used within the circuit design process.
The table below defines some of the different types and characteristics that can be encountered.
Use Of Fetal Stem Cells
| FETs for Use in Circuit Design | |
|---|---|
| Characteristic | Details |
| N-channel | An N channel FET has a channel made from N-type semiconductor in which the majority carriers are electrons. |
| P-channel | An P channel FET has a channel made from P-type semiconductor in which the majority carriers are holes. |
| J-FET | The J-FET or junction FET is a form of FET where the gate is formed by using a diode junction onto the channel. The isolation is maintained by ensuring that the diode junction remains reverse biased when operated within the circuit. It is a key requirement of the FET circuit design to ensure the junction remains reverse biased for satisfactory operation. |
| MOSFET | This type of field effect transistor relies on a metal oxide later between the gate and channel. It offers a very high input resistance. |
| Dual-gate MOSFET | As the name implies, this form of MOSFET has two gates. In FET circuit design, this gives additional options. |
| Enhancement mode | Enhancement mode FETs are OFF at zero gate-source voltage. They are turned on by pulling the gate voltage in the direction of the drain voltage, i.e. towards the supply rail, which is positive for N-channel devices and negative for P-channel devices. In other words by pulling the gate voltage towards the drain voltage, the number of carriers in the active layer of the channel is enhanced. |
| Depletion mode | In a depletion-mode MOSFET, the device is normally ON at zero gate-source voltage. Any gate voltage in the direction of the drain voltage will tend to deplete the active area of channel of carriers and reduce the current flowing. |
When designing an FET circuit, it is first necessary to select the required type of FET. Factors including the basic type of FET including whether it is a junction FET or MOSFET or another type as well as the mode type and other factors all need to be determined to before it is possible to proceed with the circuit design.
Use Of Feta Cheese
More Circuits & Circuit Design:
Op Amp basicsOp Amp circuitsPower supply circuitsTransistor designTransistor DarlingtonTransistor circuitsFET circuitsCircuit symbols
Return to Circuit Design menu . . .
